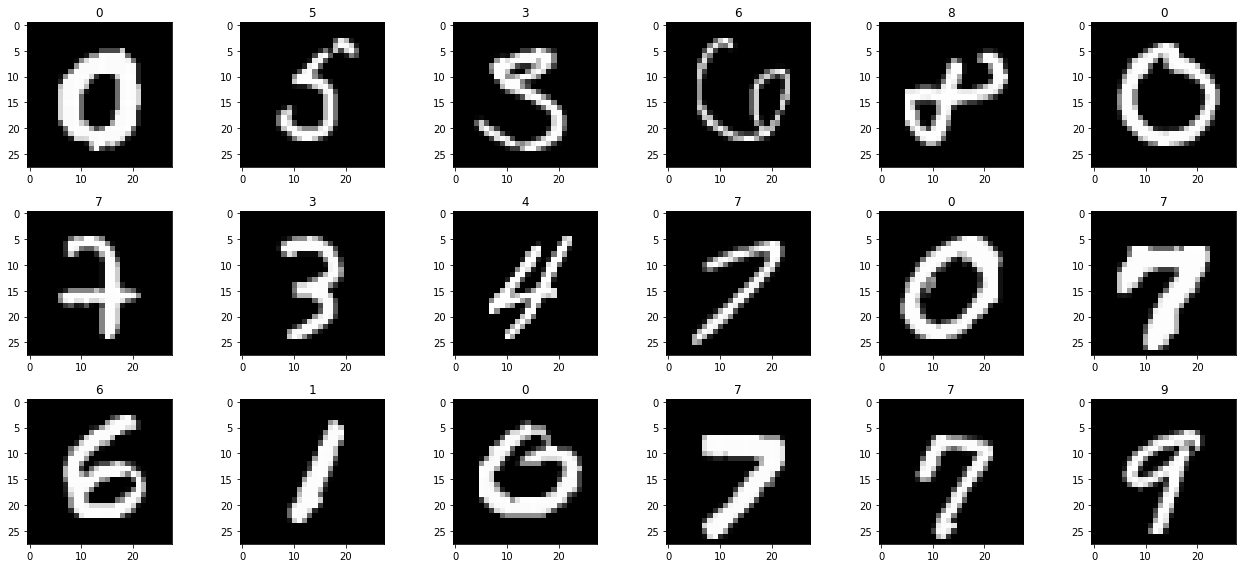Project
- Digit Recognizer Project Kaggle Competition
- Client: Kaggle
- Project date: 08 Augest, 2020
- Project URL: Digit-Recognizer-Project-Kaggle-Competition.git
- Developed and trained a model to recognize handwritten digits Achieved an accuracy of 98.93% and won a Bronze Medal for the submission on Kaggle.
About this Competition
Digit Recognizer Learn computer vision fundamentals with the famous MNIST data About this Competition The data files train.csv and test.csv contain gray-scale images of hand-drawn digits, from zero through nine. Each image is 28 pixels in height and 28 pixels in width, for a total of 784 pixels in total. Each pixel has a single pixel-value associated with it, indicating the lightness or darkness of that pixel, with higher numbers meaning darker. This pixel-value is an integer between 0 and 255, inclusive.
About the Data
The training data set, (train.csv), has 785 columns. The first column, called "label", is the digit that was drawn by the user. The rest of the columns contain the pixel-values of the associated image. Each pixel column in the training set has a name like pixelx, where x is an integer between 0 and 783, inclusive. To locate this pixel on the image, suppose that we have decomposed x as x = i * 28 + j, where i and j are integers between 0 and 27, inclusive. Then pixelx is located on row i and column j of a 28 x 28 matrix, (indexing by zero).
For example, pixel31 indicates the pixel that is in the fourth column from the left, and the second row from the top, as in the ascii-diagram below. Visually, if we omit the "pixel" prefix, the pixels make up the image like this:
The test data set, (test.csv), is the same as the training set, except that it does not contain the "label" column.
Your submission file should be in the following format: For each of the 28000 images in the test set, output a single line containing the ImageId and the digit you predict. For example, if you predict that the first image is of a 3, the second image is of a 7, and the third image is of a 8, then your submission file would look like:
Project Details
The evaluation metric for this contest is the categorization accuracy, or the proportion of test images that are correctly classified. For example, a categorization accuracy of 0.97 indicates that you have correctly classified all but 3% of the images.